AWS Mastery: 7 Ultimate Secrets to Dominate Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has revolutionized how businesses operate, and at the heart of this transformation is AWS. As the world’s most comprehensive and widely adopted cloud platform, AWS empowers startups and enterprises alike to scale, innovate, and secure their digital future like never before.
What Is AWS and Why It Dominates the Cloud

Amazon Web Services (AWS) is not just another tech platform—it’s the backbone of modern digital infrastructure. Launched in 2006 by Amazon, AWS was the first major player to offer on-demand cloud computing resources to businesses, and it has maintained its leadership ever since. Today, AWS powers millions of applications across 190 countries, serving everyone from small startups to global giants like Netflix, Airbnb, and even government agencies.
The Birth of AWS: A Game-Changer in Tech
AWS emerged from Amazon’s internal need to streamline its own infrastructure. As Amazon’s e-commerce platform grew, its engineering team realized that the scalable, modular systems they built could be offered as services to other developers. This insight led to the launch of core AWS services like Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) and EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) in 2006.
This marked a paradigm shift: instead of companies investing heavily in physical servers and data centers, they could now rent computing power, storage, and databases on a pay-as-you-go basis. This lowered the barrier to entry for innovation and sparked a wave of digital transformation across industries.
- AWS launched with just three services in 2006.
- By 2024, AWS offers over 200 fully featured services.
- It holds over 30% of the global cloud market share, ahead of Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud.
“AWS didn’t just create a new market—it redefined what’s possible in computing.” — TechCrunch
Core Components of the AWS Ecosystem
The strength of AWS lies in its breadth and depth. It’s not a single product but a vast ecosystem of interconnected services. These can be broadly categorized into compute, storage, databases, networking, machine learning, security, and developer tools.
Key foundational services include:
- Amazon EC2: Virtual servers in the cloud that can be scaled up or down in minutes.
- Amazon S3: Scalable object storage for data backup, analytics, and content delivery.
- Amazon RDS: Managed relational databases (MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, etc.).
- AWS Lambda: Serverless computing that runs code in response to events without managing servers.
These services integrate seamlessly, allowing developers to build complex applications without worrying about underlying infrastructure.
Top 7 AWS Services Every Developer Should Know
While AWS offers hundreds of services, mastering a few core ones can dramatically boost your cloud proficiency. These seven services form the foundation of most AWS architectures and are essential for anyone working in cloud computing.
1. Amazon EC2: The Backbone of AWS Compute
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) is the cornerstone of AWS’s compute offerings. It allows users to launch virtual machines—called instances—in minutes. These instances come in various sizes and types, optimized for different workloads such as general computing, memory-intensive applications, or GPU-powered machine learning.
EC2 provides complete control over computing resources, including operating system choice, networking, and security settings. With features like Auto Scaling and Elastic Load Balancing, EC2 can automatically adjust capacity to maintain performance and reduce costs during low-traffic periods.
- Over 500 instance types available for specialized needs.
- Supports Windows, Linux, and custom OS images via Amazon Machine Images (AMIs).
- Integrated with AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) for secure access control.
Learn more about EC2 capabilities at the official AWS EC2 page.
2. Amazon S3: Infinite Storage for Any Use Case
Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) is one of the most widely used cloud storage solutions in the world. Designed for 99.999999999% (11 nines) durability, S3 stores everything from website assets and backups to big data analytics datasets and AI training files.
S3 is object-based, meaning it stores data as objects within buckets (containers). Each object can be up to 5TB in size and is accessible via REST APIs, making it ideal for integration with web and mobile applications.
- Offers multiple storage classes: Standard, Intelligent-Tiering, Glacier (for archival).
- Supports versioning, lifecycle policies, and cross-region replication.
- Used by NASA to store satellite imagery and by Dropbox for user file backups.
Explore S3’s full potential at AWS S3 official documentation.
3. AWS Lambda: Revolutionizing Serverless Computing
AWS Lambda is a game-changer for developers tired of managing servers. It allows you to run code in response to events—like an HTTP request, file upload, or database change—without provisioning or managing servers. You only pay for the compute time you consume, down to the millisecond.
Lambda supports multiple programming languages, including Node.js, Python, Java, Go, and .NET. It integrates natively with other AWS services, making it perfect for building microservices, real-time data processing pipelines, and chatbots.
- No servers to manage—AWS handles scaling and availability.
- Execution duration ranges from 1ms to 15 minutes per request.
- Triggers can come from S3, DynamoDB, API Gateway, and more.
For developers, Lambda reduces operational overhead and accelerates time-to-market. Read more at AWS Lambda overview.
How AWS Transforms Business Operations
Organizations of all sizes leverage AWS to improve agility, reduce costs, and accelerate innovation. Unlike traditional IT models that require large upfront investments, AWS enables businesses to experiment, iterate, and scale with minimal risk.
Cost Efficiency and Pay-as-You-Go Pricing
One of the biggest advantages of AWS is its flexible pricing model. Instead of buying expensive hardware that may sit idle, companies pay only for the resources they use. This is particularly beneficial for startups and seasonal businesses.
AWS offers several pricing options:
- On-Demand: Pay per second with no commitment.
- Reserved Instances: Save up to 75% with 1- or 3-year commitments.
- Spot Instances: Bid on unused EC2 capacity for up to 90% off.
Additionally, AWS provides tools like the AWS Pricing Calculator and Cost Explorer to help organizations forecast and optimize spending.
“Migrating to AWS reduced our IT costs by 40% while improving performance.” — CTO, Mid-Sized SaaS Company
Global Infrastructure and High Availability
AWS operates in 33 geographic regions worldwide, with over 100 Availability Zones (AZs)—physically separate data centers within regions. This global footprint enables businesses to deploy applications close to their users, reducing latency and improving user experience.
Each AZ is designed for fault isolation, meaning an outage in one zone doesn’t affect others. By distributing workloads across multiple AZs, companies can achieve high availability and disaster recovery with minimal downtime.
- Regions include North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East, and South America.
- New regions are regularly added to meet local data sovereignty laws.
- Edge locations (via Amazon CloudFront) deliver content faster using a global CDN.
This infrastructure makes AWS a trusted choice for mission-critical applications in finance, healthcare, and e-commerce.
Security and Compliance in AWS
Security is AWS’s top priority. The platform is designed with a shared responsibility model: AWS secures the infrastructure, while customers secure their data, applications, and access controls.
AWS Shared Responsibility Model Explained
Understanding the shared responsibility model is crucial for maintaining a secure environment. AWS is responsible for:
- Physical security of data centers.
- Hardware, software, and network infrastructure.
- Availability and integrity of global infrastructure.
Customers are responsible for:
- Configuring firewalls (Security Groups and NACLs).
- Managing user access via IAM policies.
- Encrypting data at rest and in transit.
- Patching guest operating systems and applications.
This model ensures that both AWS and the customer play active roles in security, reducing the risk of breaches due to misconfigurations.
Key Security Services in AWS
AWS provides a robust suite of security tools to help organizations protect their cloud environments:
- AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM): Controls user permissions and access to AWS resources.
- AWS Key Management Service (KMS): Manages encryption keys for data protection.
- AWS Shield: Protects against DDoS attacks.
- AWS WAF: Filters malicious web traffic.
- AWS Config: Tracks configuration changes and ensures compliance.
- Amazon GuardDuty: Uses machine learning to detect threats and unauthorized behavior.
These services work together to provide defense-in-depth security, helping organizations meet compliance standards like GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2, and PCI-DSS.
“With AWS, we achieved SOC 2 compliance in just 3 months—something that would have taken years on-premises.” — Security Officer, Fintech Startup
Machine Learning and AI Powered by AWS
AWS is not just about infrastructure—it’s a leader in democratizing artificial intelligence and machine learning. Through managed services, AWS enables developers and data scientists to build, train, and deploy ML models without deep expertise in data science.
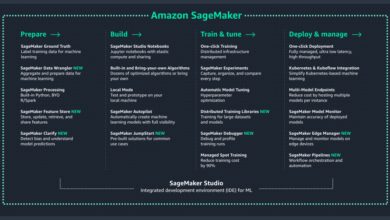
Amazon SageMaker: Build ML Models Faster
Amazon SageMaker is a fully managed service that covers the entire machine learning workflow—from data labeling and model training to deployment and monitoring. It provides Jupyter notebooks, built-in algorithms, and automatic model tuning (hyperparameter optimization).
SageMaker reduces the time to train and deploy models from weeks to hours. It integrates with data sources like S3 and Redshift and supports popular frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and MXNet.
- Used by BMW to predict maintenance needs in vehicles.
- Helps healthcare providers analyze medical images for early diagnosis.
- Enables e-commerce platforms to personalize product recommendations.
Learn more at Amazon SageMaker official site.
AI Services for Developers Without ML Expertise
For teams without data science backgrounds, AWS offers pre-built AI services that can be integrated via APIs:
- Amazon Rekognition: Image and video analysis (face detection, object recognition).
- Amazon Polly: Text-to-speech with lifelike voices.
- Amazon Transcribe: Speech-to-text transcription.
- Amazon Comprehend: Natural language processing for sentiment analysis.
- Amazon Lex: Powers conversational chatbots (used in Amazon Alexa).
These services allow developers to add intelligent features to applications quickly, such as automated customer support, content moderation, and voice-enabled interfaces.
DevOps and Automation with AWS
DevOps practices are essential for modern software delivery, and AWS provides a comprehensive set of tools to automate development, testing, deployment, and monitoring.
AWS CodePipeline and CI/CD Automation
AWS CodePipeline is a fully managed continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) service. It automates the release process, allowing developers to release updates rapidly and reliably.
A typical pipeline includes stages like:
- Source (pulling code from GitHub, AWS CodeCommit, or Bitbucket).
- Build (using AWS CodeBuild to compile and test code).
- Deploy (using AWS CodeDeploy to push to EC2, Lambda, or ECS).
- Approval (manual or automated gates).
This automation reduces human error, speeds up releases, and improves software quality.
Infrastructure as Code with AWS CloudFormation
Managing cloud resources manually is error-prone and unsustainable at scale. AWS CloudFormation allows you to define your entire infrastructure—servers, networks, databases, load balancers—as code using JSON or YAML templates.
Benefits include:
- Reproducible environments (dev, staging, production).
- Version control and audit trails.
- Faster deployment and rollback capabilities.
CloudFormation ensures consistency across environments and enables teams to treat infrastructure like software—testable, versioned, and collaborative.
“Using CloudFormation cut our deployment time from 8 hours to 15 minutes.” — DevOps Engineer, Enterprise Tech Firm
The Future of AWS: Trends and Innovations
AWS continues to innovate at a rapid pace, shaping the future of cloud computing. From edge computing to quantum computing, AWS is investing in next-generation technologies that will redefine what’s possible.
AWS Outposts: Bridging Cloud and On-Premises
Not all workloads can move to the cloud due to latency, data residency, or regulatory requirements. AWS Outposts addresses this by bringing native AWS services, infrastructure, and APIs into on-premises data centers.
Outposts enables hybrid cloud architectures where applications can run seamlessly across cloud and on-prem environments using the same tools and APIs. This is ideal for industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and finance that require low-latency processing or local data control.
- Full integration with AWS management tools (CloudFormation, IAM, etc.).
- Supports EC2, EBS, S3, and Kubernetes (EKS).
- Managed and monitored by AWS.
Discover more at AWS Outposts page.
Amazon Quantum Ledger Database (QLDB)
For applications requiring immutable and cryptographically verifiable transaction logs, AWS offers Amazon QLDB. It’s a fully managed ledger database that maintains a complete history of all changes, making it ideal for financial systems, supply chain tracking, and compliance auditing.
Unlike blockchain, QLDB is centralized and managed by AWS, offering better performance and ease of use while retaining the benefits of immutability.
- Uses a journal-based structure for transparent data changes.
- Integrates with IAM and KMS for security.
- Provides SQL-like query language (PartiQL).
QLDB is a glimpse into how AWS is reimagining databases for trust and transparency.
Getting Started with AWS: A Practical Guide
Whether you’re a developer, IT professional, or business leader, starting with AWS is easier than ever. AWS offers free tiers, training resources, and support to help you get up and running.
AWS Free Tier: Learn Without Spending
The AWS Free Tier is a powerful onboarding tool. It includes:
- 12 months of free access to popular services (EC2, S3, RDS, Lambda).
- Always-free services (e.g., 1 million Lambda requests/month, 5GB S3 storage).
- Free access to AWS Lambda, DynamoDB, and API Gateway.
This allows individuals and startups to experiment, build prototypes, and even run small production workloads at no cost.
Sign up at AWS Free Tier and start exploring.
AWS Training and Certification Paths
AWS offers a structured learning path through AWS Training and Certification. Popular certifications include:
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate: Ideal for designing distributed systems.
- AWS Certified Developer – Associate: Focuses on developing and maintaining AWS applications.
- AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate: For operations and deployment.
- AWS Certified DevOps Engineer – Professional: Advanced automation and CI/CD skills.
These certifications are globally recognized and can significantly boost career prospects in cloud computing.
Explore learning paths at AWS Training.
What is AWS used for?
AWS is used for a wide range of applications, including hosting websites and web apps, storing and analyzing big data, running machine learning models, powering mobile backends, and supporting enterprise IT systems. Its flexibility makes it suitable for nearly any computing need.
Is AWS difficult to learn?
While AWS has a steep learning curve due to its vast array of services, beginners can start with core offerings like EC2, S3, and Lambda. With free resources, hands-on labs, and structured certifications, many learners become proficient within a few months.
How does AWS compare to Azure and Google Cloud?
AWS leads in market share, service breadth, and global infrastructure. Azure excels in integration with Microsoft products, while Google Cloud is strong in data analytics and AI. The best choice depends on specific business needs, existing tech stack, and budget.
Can I use AWS for free?
Yes, AWS offers a Free Tier that includes 12 months of free access to key services, plus always-free usage limits. This is ideal for learning, testing, and small-scale projects.
What industries use AWS?
AWS is used across industries including technology, finance, healthcare, media, retail, education, and government. Companies like Netflix, Unilever, and the U.S. Department of Defense rely on AWS for critical operations.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) has redefined the digital landscape by offering scalable, secure, and innovative cloud solutions. From startups to Fortune 500 companies, AWS enables organizations to build faster, operate efficiently, and innovate with confidence. With its vast service portfolio, global infrastructure, and commitment to security and sustainability, AWS remains the leader in cloud computing. Whether you’re just starting out or scaling a global application, AWS provides the tools and support to succeed in the digital age.
Further Reading: