AWS Cloud: 7 Powerful Reasons to Dominate the Future
Welcome to the world of AWS Cloud, where innovation meets scalability. Whether you’re a startup or a global enterprise, Amazon’s cloud platform offers unmatched flexibility, security, and performance to power your digital transformation.
What Is AWS Cloud and Why It Matters

Amazon Web Services (AWS) Cloud is the world’s most comprehensive and widely adopted cloud platform. Launched in 2006, AWS provides over 200 fully featured services from global data centers, serving millions of customers—including startups, enterprises, and public sector organizations. The aws cloud infrastructure enables businesses to scale faster, reduce costs, and innovate with agility.
History and Evolution of AWS Cloud
AWS began as an internal project to improve Amazon’s own infrastructure but quickly evolved into a public cloud service. In 2006, it launched three core services: Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service), Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud), and Amazon SQS (Simple Queue Service). These laid the foundation for modern cloud computing.
- 2006: Launch of AWS with EC2, S3, and SQS
- 2010: Introduction of AWS Management Console for easier access
- 2014: AWS reaches 1 million active customers
- 2020: AWS generates over $45 billion in revenue
Today, AWS operates in 33 geographic regions with 102 Availability Zones, with more planned. This global footprint ensures low latency and high availability for users worldwide. For more details, visit the official AWS About page.
Core Components of AWS Cloud
The aws cloud ecosystem is built on a layered architecture that supports compute, storage, networking, databases, analytics, machine learning, and more. Key components include:
- Compute: Services like EC2, Lambda, and ECS enable scalable processing power.
- Storage: S3, EBS, and Glacier provide durable, secure, and cost-effective storage solutions.
- Networking: VPC, CloudFront, and Route 53 manage connectivity and content delivery.
- Security & Identity: IAM, KMS, and Shield protect data and access.
AWS isn’t just a cloud provider—it’s a complete platform for innovation, enabling developers to build virtually anything in the cloud.
Top 7 Benefits of Using AWS Cloud
Organizations choose AWS Cloud for its robust capabilities and proven track record. Here are seven powerful reasons why AWS dominates the cloud landscape.
1. Scalability and Elasticity
One of the most compelling advantages of the aws cloud is its ability to scale resources up or down based on demand. This elasticity allows businesses to handle traffic spikes without over-provisioning hardware.
- Auto Scaling adjusts compute capacity automatically.
- Load Balancers distribute traffic across multiple instances.
- Serverless options like AWS Lambda scale to zero when idle, reducing costs.
For example, Netflix uses AWS to handle millions of concurrent streams during peak hours, scaling seamlessly without service interruption.
2. Cost Efficiency and Pay-as-You-Go Model
AWS operates on a pay-as-you-go pricing model, meaning you only pay for what you use. This eliminates the need for large upfront investments in physical hardware.
- No long-term contracts or upfront commitments.
- Reserved Instances offer up to 75% savings for predictable workloads.
- Savings Plans provide flexible pricing for steady usage.
Additionally, AWS offers a detailed pricing calculator to estimate costs before deployment, helping organizations budget effectively.
3. Global Reach and High Availability
With 33 geographic regions and 102 Availability Zones (AZs), AWS provides one of the most extensive global infrastructures in the industry.
- Each region is isolated for fault tolerance.
- Each AZ within a region is physically separate, ensuring redundancy.
- Edge locations (via CloudFront) deliver content faster to end-users.
This architecture supports high availability and disaster recovery strategies, minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity.
4. Security and Compliance Leadership
Security is a top priority for AWS. The platform is designed to meet the strictest compliance requirements, including HIPAA, GDPR, SOC, and ISO standards.
- AWS Shared Responsibility Model defines security roles between AWS and customers.
- Advanced tools like AWS Shield (DDoS protection) and GuardDuty (threat detection) enhance security.
- Encryption at rest and in transit is standard across services.
Government agencies, financial institutions, and healthcare providers trust AWS due to its rigorous security posture. Learn more at AWS Security Center.
5. Innovation and Broad Service Portfolio
AWS continuously innovates, launching hundreds of new features and services each year. It offers the broadest set of tools for AI, machine learning, IoT, and analytics.
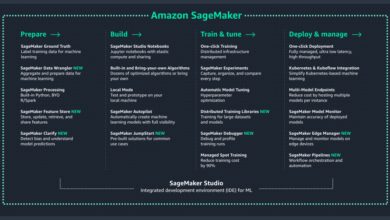
- Amazon SageMaker simplifies machine learning model development.
- AWS IoT Core connects billions of devices securely.
- Amazon Redshift enables petabyte-scale data warehousing.
This innovation allows developers to experiment and deploy cutting-edge solutions faster than ever.
6. Reliability and Uptime Performance
AWS is engineered for reliability, with many services offering 99.99% uptime SLAs. Its distributed architecture ensures that failures in one component don’t bring down entire systems.
- Multi-AZ deployments for databases like RDS improve fault tolerance.
- Automated backups and snapshots enhance data durability.
- Route 53 DNS service has a proven track record of high availability.
Companies like Airbnb and Slack rely on AWS for mission-critical applications that require uninterrupted service.
7. Strong Ecosystem and Community Support
AWS has a vast ecosystem of partners, consultants, and a thriving developer community. This support network accelerates learning and problem-solving.
- AWS Marketplace offers thousands of third-party software solutions.
- AWS Training and Certification programs help professionals build skills.
- Active forums, documentation, and re:Invent conferences foster knowledge sharing.
The community-driven approach makes it easier for new users to get started and for experts to stay ahead.
Key AWS Cloud Services You Should Know
Understanding the core services of aws cloud is essential for leveraging its full potential. Below are some of the most widely used services across industries.
Amazon EC2: Virtual Servers in the Cloud
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) provides scalable virtual servers (instances) in the cloud. Users can choose from a wide range of instance types optimized for different workloads—general purpose, compute-optimized, memory-intensive, GPU-based, and more.
- On-Demand Instances for short-term needs.
- Spot Instances for up to 90% cost savings on flexible workloads.
- Dedicated Hosts for regulatory or licensing requirements.
EC2 integrates with Auto Scaling, Elastic Load Balancing, and IAM for secure, automated infrastructure management.
Amazon S3: Scalable Object Storage
Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) is a highly durable, secure, and scalable object storage service. It’s used for storing everything from backups and logs to images, videos, and big data sets.
- Designed for 99.999999999% (11 nines) durability.
- Supports lifecycle policies to move data to cheaper tiers like S3 Glacier.
- Enables static website hosting and integration with CloudFront for fast delivery.
S3 is the backbone of many data lakes and backup strategies. Explore more at Amazon S3 official page.
AWS Lambda: Serverless Computing Power
AWS Lambda lets you run code without provisioning or managing servers. It automatically scales and runs code in response to events, charging only for the compute time consumed.
- Ideal for microservices, real-time file processing, and chatbots.
- Supports multiple languages: Python, Node.js, Java, Go, and .NET.
- Integrates seamlessly with S3, DynamoDB, API Gateway, and more.
Lambda reduces operational overhead and accelerates development cycles, making it a favorite among DevOps teams.
How AWS Cloud Supports Digital Transformation
Digital transformation is no longer optional—it’s essential for survival in today’s competitive landscape. The aws cloud acts as a catalyst by enabling organizations to modernize legacy systems, adopt agile practices, and deliver customer-centric solutions faster.
Modernizing Legacy Applications
Many enterprises still rely on outdated on-premises systems that are costly to maintain and hard to scale. AWS offers several strategies to modernize these applications:
- Rehosting (lift-and-shift): Move applications to EC2 with minimal changes.
- Refactoring: Re-architect apps to use cloud-native services like Lambda and RDS.
- Containerization: Use Amazon ECS or EKS to run containerized apps at scale.
For example, Capital One migrated its entire infrastructure to AWS, enabling faster innovation and improved customer experiences.
Enabling Agile Development and DevOps
AWS supports DevOps practices through integrated tools like AWS CodePipeline, CodeBuild, and CodeDeploy. These enable continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD), reducing release cycles from weeks to minutes.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC) via AWS CloudFormation or Terraform.
- Monitoring and logging with CloudWatch and X-Ray.
- Automated testing and deployment pipelines.
This agility allows teams to experiment, fail fast, and iterate quickly—key principles of modern software development.
Accelerating Data-Driven Decision Making
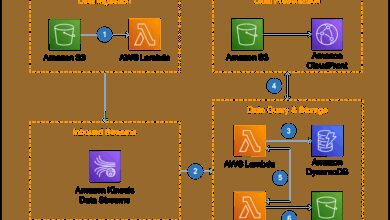
Data is the new oil, and AWS provides powerful tools to collect, process, and analyze it. Services like Amazon Kinesis, Redshift, and QuickSight turn raw data into actionable insights.
- Kinesis streams real-time data from applications and devices.
- Redshift performs complex queries on large datasets.
- QuickSight delivers interactive dashboards and machine learning-powered insights.
With AWS, businesses can move from reactive to proactive decision-making, gaining a competitive edge.
AWS Cloud Security: Best Practices and Tools
Security in the aws cloud follows the Shared Responsibility Model: AWS secures the infrastructure, while customers secure their data, applications, and access.
Understanding the Shared Responsibility Model
This model clearly defines who is responsible for what:
- AWS Responsibilities: Physical security, hardware, software, networking, and virtualization.
- Customer Responsibilities: Firewall configuration, encryption, IAM policies, patch management, and data classification.
For example, AWS manages the security of the EC2 hypervisor, but the customer must secure the operating system and applications running on the instance.
Essential Security Services on AWS
AWS offers a suite of native tools to help customers secure their environments:
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Controls user access with policies and roles.
- Key Management Service (KMS): Manages encryption keys for data protection.
- Security Hub: Provides a comprehensive view of security alerts and compliance status.
- WAF and Shield: Protect web applications from common exploits and DDoS attacks.
Using these tools together creates a defense-in-depth strategy that minimizes risk.
Implementing Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust is a security framework that assumes no user or device should be trusted by default, even inside the network. AWS supports Zero Trust through:
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all users.
- Network segmentation using VPCs and security groups.
- Continuous monitoring with GuardDuty and CloudTrail.
- Just-in-time access via AWS Systems Manager.
Adopting Zero Trust on AWS enhances protection against insider threats and lateral movement by attackers.
Migration to AWS Cloud: Strategies and Best Practices
Migrating to the aws cloud can be complex, but with the right strategy, it can deliver significant benefits. AWS recommends the 6R migration framework.
The 6R Migration Framework
Developed by AWS, the 6Rs provide a structured approach to cloud migration:
- Rehost: Move applications as-is (lift-and-shift).
- Refactor: Modify apps to take advantage of cloud-native features.
- Rearchitect: Redesign applications for scalability and resilience.
- Replatform: Make minor optimizations (e.g., moving to RDS).
- Retire: Decommission unused or redundant applications.
- Retain: Keep certain apps on-premises for now.
This framework helps organizations prioritize efforts and allocate resources effectively.
Using AWS Migration Services
AWS provides specialized tools to streamline migration:
- AWS Server Migration Service (SMS): Automates replication of on-premises VMs.
- Database Migration Service (DMS): Migrates databases with minimal downtime.
- Application Discovery Service: Identifies on-premises assets and dependencies.
- CloudEndure Migration: Enables near-zero downtime migration.
These tools reduce risk and accelerate the migration timeline. Learn more at AWS Migration Hub.
Avoiding Common Migration Pitfalls
Despite the benefits, cloud migrations can fail due to poor planning. Common pitfalls include:
- Underestimating data transfer costs and time.
- Ignoring application dependencies.
- Failing to optimize workloads post-migration.
- Lack of skills and training for cloud operations.
To avoid these, organizations should conduct thorough assessments, involve stakeholders early, and invest in training and change management.
Future Trends in AWS Cloud and Cloud Computing
The aws cloud is not standing still. Amazon continues to push boundaries in AI, edge computing, sustainability, and hybrid cloud solutions.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
AWS is embedding AI/ML into its core services. Amazon Bedrock allows access to foundation models, while SageMaker Autopilot automates model building.
- AI-powered analytics in QuickSight and Lex for chatbots.
- Personalization engines for retail and media.
- Generative AI tools for content creation and code generation.
These advancements make AI accessible even to non-experts, democratizing innovation.
Edge Computing with AWS Wavelength and Outposts
To reduce latency for real-time applications, AWS offers edge solutions:
- AWS Wavelength: Embeds AWS services within 5G networks for ultra-low latency.
- AWS Outposts: Brings AWS infrastructure and services on-premises.
- AWS Snow Family: Portable devices for data collection and processing in remote locations.
These are ideal for autonomous vehicles, AR/VR, and industrial IoT applications.
Sustainability and Green Cloud Initiatives
AWS is committed to sustainability, aiming to power its operations with 100% renewable energy by 2025.
- Energy-efficient data centers with advanced cooling systems.
- Carbon footprint tool to track emissions.
- Partnerships with wind and solar farms globally.
By choosing AWS, organizations can reduce their environmental impact while benefiting from efficient infrastructure.
What is AWS Cloud?
AWS Cloud is Amazon’s cloud computing platform that provides on-demand IT resources like servers, storage, databases, and AI tools over the internet, allowing businesses to scale and innovate efficiently.
How much does AWS Cloud cost?
AWS uses a pay-as-you-go model with no upfront fees. Costs depend on usage, but free tier options are available for new users. Detailed pricing can be calculated using the AWS Pricing Calculator.
Is AWS Cloud secure?
Yes, AWS Cloud is highly secure, offering encryption, identity management, DDoS protection, and compliance with global standards like GDPR and HIPAA. Security is shared between AWS and the customer.
Can I migrate my existing apps to AWS?
Yes, AWS supports migration of existing applications using tools like Server Migration Service, Database Migration Service, and Application Discovery Service, with strategies ranging from lift-and-shift to full re-architecture.
What industries use AWS Cloud?
AWS is used across industries including finance, healthcare, retail, media, government, and education, serving companies like Netflix, Airbnb, and the NFL.
In conclusion, AWS Cloud stands as a transformative force in modern technology. From its unmatched scalability and security to its vast array of services and global reach, AWS empowers organizations to innovate faster, operate more efficiently, and stay ahead in a digital-first world. Whether you’re just starting your cloud journey or optimizing an existing setup, AWS provides the tools, support, and vision to turn ideas into reality. The future of computing is in the cloud—and AWS is leading the way.
Further Reading: